Windows XP Professional comes with a powerful command-line tool called Tasklist that provides many details on the programs and processes that are running.
Tasklist can be applied to see how much memory and CPU time running processes are using, what DLL files they rely on, and other information. Thus it can be a very useful troubleshooting tool.
Basic Tasklist command
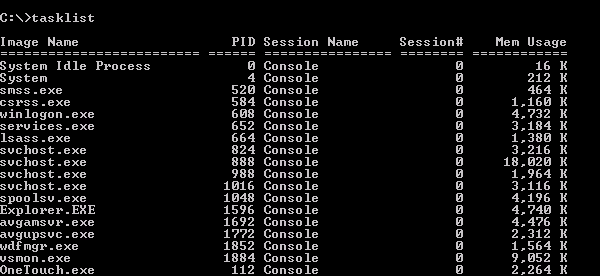
If all you want to know is what tasks are running, enter TASKLIST into the command line. The output can be redirected to a file if you wish. The default format is a table with several columns of information. An example of a partial console output is shown in the figure below. There are five columns of information. The following list gives the meanings of the various column headings:
- Image Name
- The name of the process or the executable file running the process.
- PID
- The process ID. The system assigns a number to each process so it can keep track of it. It is possible to have several processes running with identical names but the PID will be unique. Note that the PID may not be the same each time you open a particular program. You may need the PID to run certain other diagnostic tools and Tasklist is one way to obtain this information.
- Session Name
- Unless you are on a network, this will read “Console” indicating that the process was started locally. Home PC users can usually ignore this column.
- Session#
- Each session is assigned a number. Home PC users can usually ignore this column also.
- Mem Usage
- This gives the very useful information about how much memory (in KB) that a process was using at the time Tasklist was run.